| Note: This tutorial assumes that you have completed the previous tutorials: ROS Tutorials. |
| |
Arduino IDE Setup
Description: This tutorial shows step-by-step how to setup up the Arduino IDE to use rosserial.Tutorial Level: BEGINNER
Next Tutorial: Hello World (example publisher)
Contents
Introduction
The Arduino and Arduino IDE are great tools for quickly and easily programming hardware. Using the rosserial_arduino package, you can use ROS directly with the Arduino IDE. rosserial provides a ROS communication protocol that works over your Arduino's UART. It allows your Arduino to be a full fledged ROS node which can directly publish and subscribe to ROS messages, publish TF transforms, and get the ROS system time.
NOTE: If you do not already have an Arduino IDE installed, download it from the Arduino website. It is best to install the application into a folder on the application PATH, the desktop, or home folder. Once installed, launch the application to select your sketchbook location. (See arduino official website, sketchbook is a standard place to store your programs, or sketches). Close the IDE when done.
Our ROS bindings are implemented as an Arduino library. Like all Arduino libraries, ros_lib works by putting its library implementation into the libraries folder of your sketchbook. If there is not already a libraries folder in your sketchbook, make one. You can then install the library using the instructions below.
In order to use the rosserial libraries in your own code, you must first put
#include <ros.h>
prior to including any other header files, e.g.
#include <std_msgs/String.h>
otherwise the Arduino IDE will not be able to locate them.
Installing the Software
Installing on the ROS workstation
You have 2 options of how to install related libraries.
(RECOMMENDED) Installing Binaries on the ROS workstation
You can install rosserial for Arduino by running:
sudo apt-get install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-rosserial-arduino
sudo apt-get install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-rosserial
Installing from Source onto the ROS workstation
Source build instructions are different for groovy+ (catkin) than for earlier (rosbuild) releases. Select the build system based on your release to see appropriate instructions.
Rosserial has been catkin-ized since the groovy release, and the workflow is a bit different from fuerte and earlier releases. Rather than running the library generator over each package you want to use, you run it once and generate libraries for all installed messages. In the instructions below, <ws> represents your catkin workspace.
cd <ws>/src git clone https://github.com/ros-drivers/rosserial.git cd <ws> catkin_make catkin_make install
These commands clone rosserial from the github repository, generate the rosserial_msgs needed for communication, and make the library files in the <ws>/devel/lib directory.
Note: currently you HAVE to run catkin_make install, otherwise portions of the ros_lib directory will be missing. This will hopefully be fixed soon.
hg clone https://kforge.ros.org/rosserial/hg rosserial rosmake rosserial_arduino
These commands clone rosserial from the kforge repository using mercurial, generate the rosserial_msgs needed for communication, and make the ros_lib library.
Install ros_lib into the Arduino Environment
The preceding installation steps created the necessary libraries, now the following will create the ros_lib folder that the Arduino build environment needs to enable Arduino programs to interact with ROS.
In the steps below, <sketchbook> is the directory where the Linux Arduino environment saves your sketches. Typically this is a directory called sketchbook or Arduino in your home directory. e.g cd ~/Arduino/libraries
Alternately, you can install into a Windows Arduino environment.
Ros_lib installation instructions are different for groovy source (catkin) than for earlier (rosbuild) or binary releases. Be sure you've selected the correct build system above to see appropriate instructions - catkin for a groovy source build, rosbuild otherwise.
Note: you have to delete libraries/ros_lib, if present, in order to regenerate as its existence causes an error. "rosrun rosserial_arduino make_libraries.py" creates the ros_lib directory.
cd <sketchbook>/libraries rm -rf ros_lib rosrun rosserial_arduino make_libraries.py .
If you are building the Arduino on Windows, you need to create the ros_lib folder in some convenient directory.
cd <some_empty_directory> rosrun rosserial_arduino make_libraries.py .
Now that you've installed either from source or debs, all you have to do is copy the rosserial_arduino/libraries directory into your Arduino sketchbook:
roscd rosserial_arduino/src cp -r ros_lib <sketchbook>/libraries/ros_lib
If you are building Arduino on Windows, copy the ros_lib directory from Linux to the Windows sytem's sketchbook/libraries folder (typically found in My Documents).
*Note: Currently you can install the Arduino libaries directly in the Arduino IDE. Just open the Library Manager from the IDE menu in Sketch -> Include Library -> Manage Library. Then search for "rosserial". This is useful if you need to work on an Arduino sketch but don't want to setup a full ROS workstation.
Finishing Up
After restarting your IDE, you should see ros_lib listed under examples:
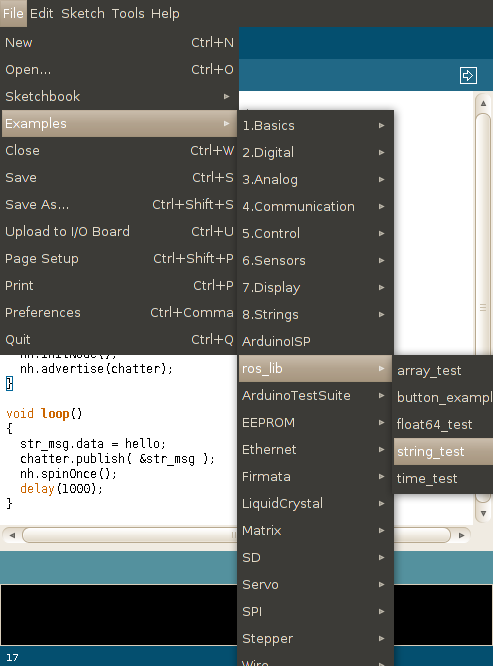
And under Windows:








